Blockchain technology has evolved from a niche concept linked to cryptocurrency to a revolutionary force transforming industries across the globe. In its simplest form, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger used to record transactions across many computers. This technology is seen as secure and tamper-resistant due to its design. But how exactly does it work? This article will explore the inner workings of blockchain technology, its key components, and its potential applications beyond cryptocurrencies.
Understanding Blockchain: The Basics
At its core, blockchain technology is based on a structure of blocks that are linked together, forming a chain. Each block contains a set of transactions that are recorded and verified. The “block” is like a page in a digital ledger, and the “chain” refers to the links that connect each page. These blocks are cryptographically secured, meaning that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be changed or tampered with, which ensures the integrity of the data stored.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
To better understand how blockchain works, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the key features that make it distinct from traditional databases.
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authority (like a bank or government) controls data, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers. These computers, known as nodes, collaborate to validate and record transactions. This distributed nature removes the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing transparency.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded in a block and added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures that data stored on a blockchain remains permanent and reliable, making it an ideal choice for financial transactions, contracts, and records.
- Transparency and Security: Blockchain provides a transparent and secure system. All participants in the network can access the blockchain and view the transaction history. While the details of the transactions are available, the identities of the parties involved are encrypted, ensuring privacy while promoting transparency.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks rely on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions. These are the rules or protocols that ensure all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. The most common consensus mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
How Blockchain Works: The Process
Let’s walk through the step-by-step process of how blockchain works, from the initiation of a transaction to its final confirmation.
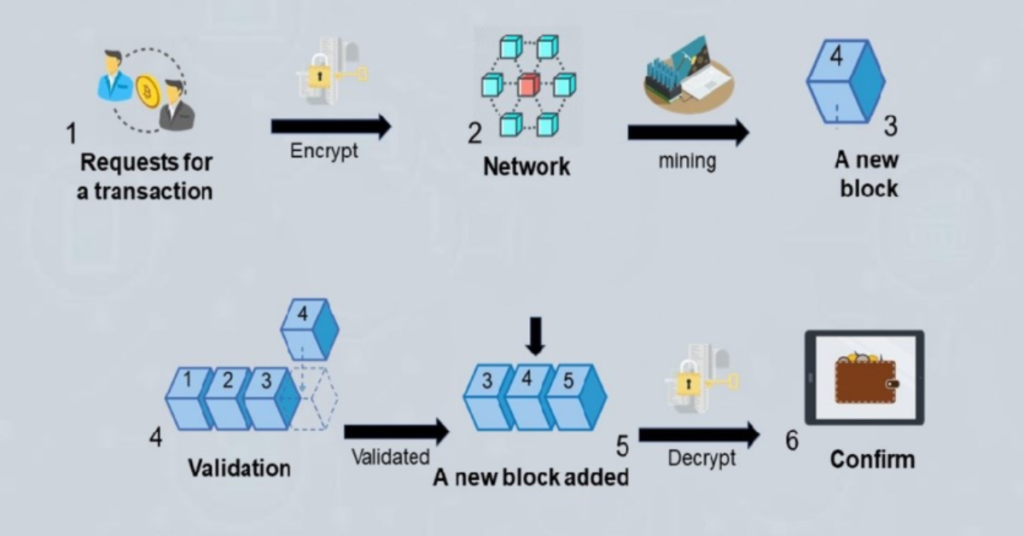
1. Transaction Initiation
The first step in the blockchain process is the initiation of a transaction. This could be any kind of data exchange, such as a transfer of cryptocurrency, a smart contract execution, or even the recording of a supply chain event. A user initiates the transaction by creating a “block” containing their request, such as sending Bitcoin to another user. Each transaction is digitally signed to verify the identity of the sender.
2. Transaction Validation
After the transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to a network of nodes. Each node is responsible for validating the transaction. This is done through consensus algorithms, such as PoW or PoS, to ensure that the transaction is legitimate and that the sender has the necessary funds or authority.
In Proof of Work, miners (computers on the network) compete to solve complex mathematical problems. The first miner to solve the problem gets the right to add the new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency. In Proof of Stake, validators are chosen to create a new block based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
3. Block Creation and Addition
Once the transaction is validated by the nodes, it is bundled together with other transactions into a block. This block is then added to the blockchain in a linear and chronological order. Because each block contains a reference (hash) to the previous block, the chain of blocks is unbreakable, ensuring that no transaction can be tampered with once it’s been added to the chain.
4. Block Confirmation and Distribution
After a block is added to the blockchain, it is distributed across the network. All participants in the blockchain are able to access the updated version of the ledger, ensuring that everyone has the same, up-to-date record of transactions. This decentralized distribution makes it difficult for any single entity to alter or delete the data.
5. Finality
Once the block is added to the chain and confirmed, the transaction is considered final. Because the blockchain is immutable, the transaction cannot be reversed or altered. This provides a high level of security for both parties involved.
Key Terms and Concepts in Blockchain Technology
To gain a deeper understanding of blockchain, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with some key terms and concepts that are integral to its functioning:
- Ledger: A record of transactions. In blockchain, the ledger is decentralized, meaning it is shared and updated across all nodes in the network.
- Hash: A cryptographic algorithm that converts data into a fixed-size string of characters. Each block in the blockchain contains a unique hash that links it to the previous block, ensuring the integrity of the chain.
- Cryptography: The use of mathematical techniques to secure data. Cryptography is fundamental to blockchain, as it ensures the privacy and security of transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce the conditions agreed upon by the parties without needing an intermediary.
- Mining: The process of validating and adding new blocks to the blockchain, typically associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Miners use computational power to solve complex puzzles and are rewarded for their efforts.
- Node: A computer that participates in the blockchain network. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain and works to validate transactions.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Organizations that are run by smart contracts and governed by rules encoded into blockchain technology, without the need for centralized management.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has far-reaching implications, especially beyond cryptocurrencies. Some of the key areas where blockchain is being applied include:
1. Finance and Cryptocurrency
Blockchain’s most well-known application is in the realm of cryptocurrency, with Bitcoin being the most notable example. It allows for peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. This opens the door for faster, cheaper, and more secure financial transactions, particularly for cross-border payments.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology can be used to track goods as they move through the supply chain. By recording each transaction on an immutable ledger, stakeholders can monitor the journey of products, ensuring authenticity, reducing fraud, and increasing efficiency.
3. Healthcare
Blockchain can transform the healthcare industry by securely storing patient data, improving the sharing of medical records across providers, and ensuring that healthcare transactions are tamper-proof.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain offers a potential solution to voting fraud in elections. By utilizing the immutability and transparency of the technology, blockchain-based voting systems can provide a secure and verifiable way to cast votes.
5. Intellectual Property Protection
Blockchain can be used to secure intellectual property rights, allowing creators to register their work and prove ownership. This helps prevent theft and ensures that creators receive proper compensation.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a powerful and transformative innovation that promises to reshape industries across the world. By understanding how it works—through its decentralized, transparent, and secure mechanisms—individuals and businesses can better appreciate its potential and prepare for the future. As blockchain continues to evolve, its applications and possibilities will likely expand, creating new opportunities in finance, healthcare, logistics, and beyond.




