The world of cryptocurrency can seem daunting for beginners, but once you break down its key components, it becomes much easier to understand. Cryptocurrency has rapidly gained popularity over the past decade, offering a decentralized, digital form of currency that operates outside of traditional financial systems. This guide will take you through the fundamentals of cryptocurrency, its workings, popular types, and how to get started, providing you with a solid foundation to dive deeper into the world of digital currencies.

What is Cryptocurrency?
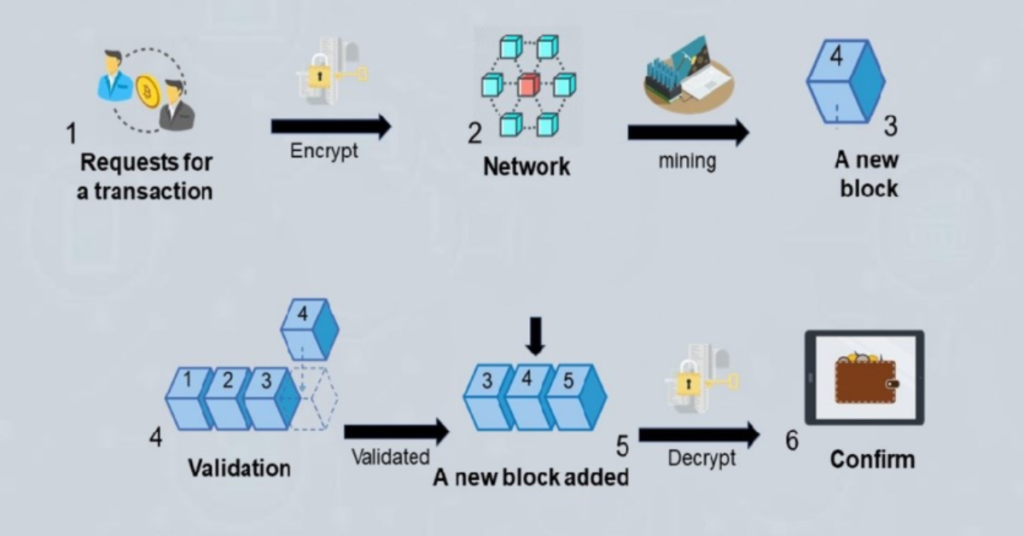
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital currency that uses cryptography for security, making it difficult to counterfeit or double-spend. Unlike traditional currencies, such as the US dollar or euro, cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized system without a central authority like a bank or government. Instead, they rely on blockchain technology to secure and verify transactions.
A cryptocurrency transaction takes place on a peer-to-peer network, meaning that it can be conducted directly between users without an intermediary. The decentralized nature of these digital currencies provides an alternative to the centralized financial systems we are familiar with.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
At the heart of most cryptocurrencies is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger—a digital database—that records all transactions across a network of computers. These transactions are grouped together in blocks, and once a block is filled, it is added to the chain in a linear, chronological order. Each new block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain. This structure makes blockchain extremely secure and nearly impossible to tamper with, providing transparency and trust in the system.
Key Features of Cryptocurrencies
Some of the defining features of cryptocurrency include:
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies are not controlled by a central authority like a bank or government, allowing users to maintain control over their finances.
- Security: Cryptography ensures the security of transactions, making it nearly impossible for hackers to alter transaction records.
- Transparency: Every transaction made with cryptocurrency is recorded on the blockchain, making it easy for users to track.
- Privacy: While transactions are public, the identities of the participants are not directly tied to their wallet addresses, offering a degree of privacy.
Popular Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, but today, there are thousands of cryptocurrencies, each with its own characteristics and use cases. Let’s take a look at some of the most popular ones:
- Bitcoin (BTC): Bitcoin is the original cryptocurrency, created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It remains the largest and most valuable cryptocurrency. Bitcoin’s primary use case is as a store of value or digital gold.
- Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Ethereum’s native currency, Ether (ETH), is used to power these applications.
- Ripple (XRP): Ripple focuses on enabling fast and cost-efficient cross-border payments. It is used by financial institutions and payment providers to facilitate quick international transactions.
- Litecoin (LTC): Often called the silver to Bitcoin’s gold, Litecoin is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency that is designed to process transactions more quickly than Bitcoin.
- Binance Coin (BNB): Binance Coin is the native currency of the Binance exchange, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges globally. BNB is used for trading fee discounts, token sales, and various other applications within the Binance ecosystem.
Other well-known cryptocurrencies include Cardano (ADA), Polkadot (DOT), Solana (SOL), and Dogecoin (DOGE), each catering to different sectors within the blockchain and cryptocurrency space.
How to Buy Cryptocurrency
Getting started with cryptocurrency is relatively easy. Here’s a step-by-step guide for beginners:
- Select a Cryptocurrency Exchange: Cryptocurrency exchanges are platforms that allow users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. Some of the most popular exchanges include Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Gemini.
- Create an Account: To use a cryptocurrency exchange, you’ll need to create an account. This usually involves providing personal information for identity verification purposes.
- Deposit Funds: Once your account is set up, you can deposit fiat currency (like USD or EUR) into your account through a bank transfer or credit card.
- Choose Your Cryptocurrency: After depositing funds, you can choose which cryptocurrency to buy. Popular options include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, but there are many others to explore.
- Store Your Cryptocurrency: Once you’ve purchased cryptocurrency, you’ll need a place to store it. While exchanges provide wallets for storing your coins, for added security, many users prefer to use a hardware wallet, which is an offline device that stores private keys securely.
Understanding Key Cryptocurrency Terms
There are several essential terms and concepts that newcomers to cryptocurrency should understand. These include:
- Blockchain: A digital ledger that records all transactions in a secure and decentralized manner.
- Wallet: A digital container that holds your cryptocurrencies. There are two types: hot wallets (online) and cold wallets (offline).
- Private Key: A private, encrypted code that grants access to your cryptocurrency. It’s crucial to keep this key safe and never share it.
- Public Key: A unique address that is used to receive cryptocurrency. Think of it like an email address where others can send you crypto.
- Mining: The process by which new cryptocurrency coins are created and transactions are added to the blockchain. Miners use computational power to solve complex mathematical problems.
- Token: A unit of cryptocurrency that represents a specific asset or utility. These can be created and managed on existing blockchain networks, such as Ethereum.
- Smart Contract: A self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Ethereum popularized smart contracts, which enable decentralized applications (DApps) to function.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A movement that uses blockchain and cryptocurrency to create decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading.
Why Cryptocurrency? Benefits and Opportunities
Cryptocurrencies offer several advantages over traditional financial systems, which has led to their rapid adoption. Some key benefits include:
- Lower Transaction Fees: Cryptocurrency transactions often come with significantly lower fees than traditional payment systems, especially for international transfers.
- Faster Transactions: Transactions made with cryptocurrency can be processed more quickly than those using banks or credit cards, particularly for cross-border payments.
- Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies provide financial access to people who are unbanked or underbanked, offering a way for individuals to participate in the global economy without a traditional bank account.
- High Investment Potential: Many investors see cryptocurrency as a store of value or a high-risk, high-reward investment opportunity. Some cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, have seen significant increases in value over time.
- Security and Privacy: Cryptocurrencies use advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and provide users with a level of privacy that traditional banking systems cannot offer.
Risks and Challenges of Cryptocurrency
Despite its potential, cryptocurrency carries certain risks that should be considered:
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile. Prices can fluctuate dramatically within short timeframes, leading to potential losses.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments and regulators are still figuring out how to regulate cryptocurrency, and future regulations may impact how cryptocurrencies are used or valued.
- Security Threats: While blockchain is inherently secure, exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacks. There have been high-profile security breaches in the past.
- No Consumer Protections: Unlike traditional banking systems, cryptocurrencies are not insured or protected by government agencies. If you lose access to your cryptocurrency wallet or fall victim to fraud, there is often no recourse.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency represents a revolutionary shift in the financial landscape, providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent alternative to traditional money. With its potential to disrupt everything from banking to investment to the very concept of money, cryptocurrencies offer exciting possibilities. However, they also come with risks, and it’s important to approach them with caution, particularly as you start your journey.
For beginners, understanding the key features, terms, and how to safely buy and store cryptocurrency is crucial. By educating yourself and staying up-to-date with developments in the space, you can better navigate the ever-changing world of digital currencies and make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Whether you’re investing, using cryptocurrency for transactions, or exploring the emerging world of decentralized finance, cryptocurrencies have the power to shape the future of money.